Appendix IV: Six Modeling Approaches
The SRES Terms of Reference call for a multi-model approach for developing
emissions scenarios (see Appendix I). In all, six different
modeling approaches were used to generate the 40 SRES scenarios. These six models
are representative of the approaches to emissions scenario modeling and the
different integrated assessment frameworks used in the scenario literature and
include both macro-economic (so-called top-down) and systems-engineering (so-called
bottom-up) models. Some modeling teams developed scenarios to reflect all four
storylines, while some presented scenarios for fewer storylines. Chapter
4 lists all the SRES scenarios, by modeling group and by scenario family.
The six modeling approaches include:
- Asian Pacific Integrated Model (AIM) from the National Institute of Environmental
Studies in Japan (Morita et al., 1994);
- Atmospheric Stabilization Framework Model (ASF) from ICF Consulting in the
USA (Lashof and Tirpak, 1990; Pepper et al., 1992, 1998; Sankovski
et al., 2000);
- Integrated Model to Assess the Greenhouse Effect (IMAGE) from the National
Institute for Public Health and Environmental Hygiene (RIVM) (Alcamo et
al., 1998; de Vries et al., 1994, 1999, 2000), used in connection
with the Dutch Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis (CPB) WorldScan model (de
Jong and Zalm, 1991), the Netherlands;
- Multiregional Approach for Resource and Industry Allocation (MARIA) from
the Science University of Tokyo in Japan (Mori and Takahashi, 1999; Mori,
2000);
- Model for Energy Supply Strategy Alternatives and their General Environmental
Impact (MESSAGE) from the International Institute of Applied Systems Analysis
(IIASA) in Austria (Messner and Strubegger, 1995; Riahi and Roehrl, 2000);
and the
- Mini Climate Assessment Model (MiniCAM) from the Pacific Northwest National
Laboratory (PNNL) in the USA (Edmonds et al., 1994, 1996a, 1996b).
IV.1. Asian Pacific Integrated Model
The Asian Pacific Integrated Model (AIM) is a large-scale computer simulation
model for scenario analyses of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and the impacts
of global warming in the Asian-Pacific region. This model is being developed
mainly to examine global warming response measures in the region, but it is
linked to a world model so that it is possible to make global estimates. AIM
comprises three main models - the GHG emission model (AIM/emission), the global
climate change model (AIM/climate), and the climate change impact model (AIM/impact).
|
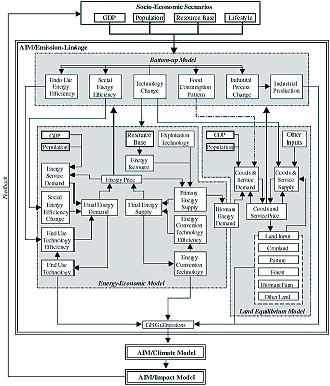
Figure IV-1: Outline of AIM/emission linkages.
|
The AIM-based quantification was conducted as an Asian collaborative
project using a new linked version of the AIM/emission model, which covers
the world but has a more detailed structure for the Asian-Pacific region
than for other regions. The new linked version couples bottom-up models
and top-down models (Figure IV-1).
| Table IV- 1: Regional disaggregation
of the six modeling approaches. |
|
| SRES |
REF
|
OECD90
|
ASIA
|
ALM
|
|
| AIM |
Economies in Transition
|
OECD- West
|
USA
|
Oceania
|
Japan
|
Korea
|
Indoesia
|
Thaiand
|
Malysia
|
Other
East
Asia
|
India
|
Other
South-
Asia
|
China
|
Other
Centrally
Planned
Asia
|
Middle
East
|
Africa
|
Latin
America
|
|
| ASF |
Centrally Planned Europe
|
OECD- West
|
USA
|
OECD
Asia-Pacific
|
South East Asia
|
Centrally
Planned Asia
|
Middle
East
|
Africa
|
Latin
America
|
|
| IMAGE |
Former Soviet Union
|
Eastern Europe
|
OECD- Europe
|
Canada
|
USA
|
Oceania
|
Japan
|
East Asia
|
South Asia
|
Centrally
Planned Asia
|
Middle
East
|
Africa
|
Latin
America
|
|
| MESSAGE |
Former Soviet Union
|
Eastern Europe
|
Western Europe
|
North America
|
Pacific OECD
|
Pacific Asia
|
South Asia
|
Centrally
Planned Asia
|
Middle East & North Africa Sub- Saharan Africa
|
Latin America
|
|
| MARIA |
Eastern Europe and Former Soviet Union
|
Other OECD
|
North Ame- rica
|
(Other OECD)
|
Japan
|
ASEAN and Other Asia
|
South Asia
|
China
|
ALM and others
|
|
| MiniCAM |
Centrally Planned Europe
|
OECD-Europe
|
Canada
|
USA
|
|
|
South East Asia
|
Centrally
Planned Asia
|
Middle
East
|
Africa
|
Latin
America
|
|
| Table IV-2: ASF regions. |
|
| Region |
Countries |
|
| Africa (AFRICA) |
All African countries |
| Centrally Planned Asia (CPASIA) |
China, Laos, Mongolia, Korea (DPR), Vietnam |
| Eastern Europe and newly independent states (EENIS) |
Albania, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, former USSR,
former Yugoslavia |
| Latin America (LAMER) |
All Latin American countries (including Mexico, Central and South America) |
| Middle East (MEAST) |
All Middle Eastern countries including Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi
Arabia, and UAE |
| OECD-East (OECDA) |
Australia, Japan, New Zealand |
| OECD-West (OECDW) |
Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland,
Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden,
Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom |
| South East Asia and Oceania (SEASIA) |
Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Republic
of Korea, Burma, Pakistan, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and other countries
of the region |
| USA (USA) |
USA, Puerto Rico, and other US territories |
|
|