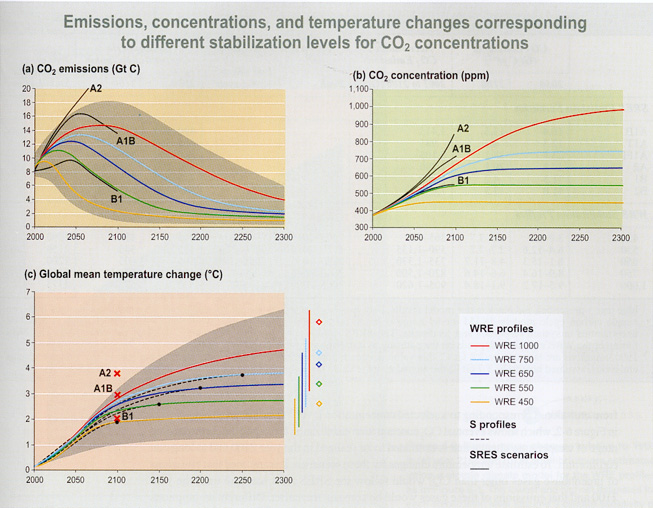
Figure 6-1: Stabilizing CO2 concentrations would require substantial
reductions of emissions below current levels and would slow the rate of warming.
- CO2 emissions: The time paths of CO2 emissions
that would lead to stabilization of the concentration of CO2
in the atmosphere at 450, 550, 650, 750, and 1,000 ppm are estimated for
the WRE stabilization profiles using carbon cycle models. Lower CO2
concentration levels would require an earlier reversal of emissions growth
and earlier decreases to levels below current emissions. The shaded area
illustrates the range of uncertainty in estimating CO2 emissions
corresponding to specified concentration time paths, as represented in carbon
cycle models. Also shown for comparison are CO2 emissions for
three of the SRES scenarios (A1B, A2, and B1), which do not include greenhouse
gas emission limits.
- CO2 concentrations: The CO2 concentrations
specified for the WRE profiles gradually approach stabilized levels that
range from 450 to 1,000 ppm. Also shown for comparison are estimates of
CO2 concentrations that would result from three of the SRES projections
of emissions (A1B, A2, and B1).
- Global mean temperature changes: Global mean temperature changes
are estimated for the WRE stabilization profiles using a simple climate
model tuned in turn to each of several more complex models.Estimated warming
slows as growth in the atmospheric concentration of CO2 slows
and warming continues after the time at which the CO2 concentration
is stabilized (indicated by black spots) but at a much diminished rate.
It is assumed that emissions of gases other than CO2 follow the
SRES A1B projection until the year 2100 and are constant thereafter.This
scenario was chosen as it is in the middle of the range of the SRES scenarios.
The dashed lines show the temperature changes projected for the S profiles,
an alternate set of CO2 stabilization profiles (not shown in
panels (a) or (b)). The shaded area illustrates the effect of a range of
climate sensitivity across the five stabilization cases.The colored bars
on the righthand side show, for each WRE profile, the range at the year
2300 due to the different climate model tunings and the diamonds on the
righthand side show the equilibrium (very long-term) warming for each stabilization
level using average climate model results. Also shown for comparison are
temperature increases in the year 2100 estimated for the SRES emission scenarios
(indicated by red crosses).
Back to text